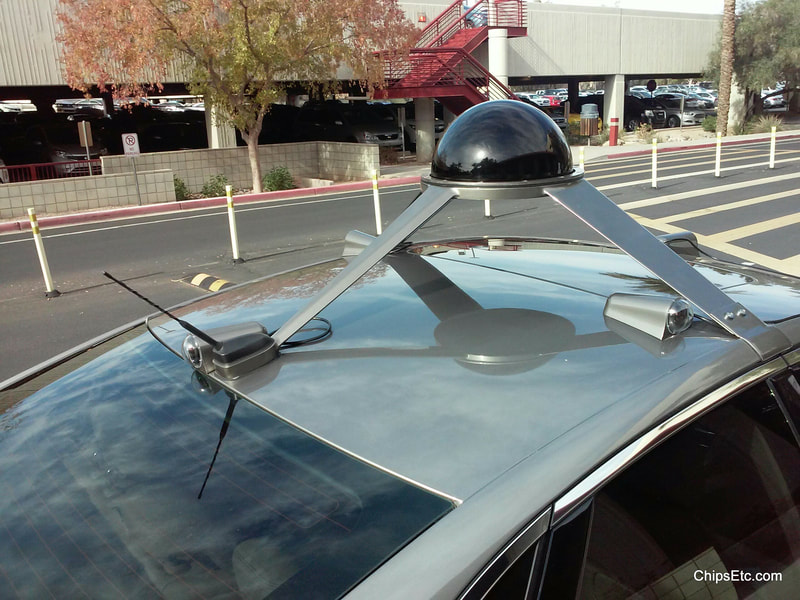
Computer chips have been used in cars since the 1970s. Soild state computers were initially used to control the engine's fuel injection system and to monitor the car's performance.
Over time, the use of computer chips in cars has expanded to include a wide range of functions, such as controlling the transmission, adjusting for best engine performance, monitoring anti-lock brakes, and providing information to the driver, ignition and remote entry security systems, as well as infotainment and GPS location / route mapping.
In recent years, computer chips have been used to enable advanced features such as autonomus driving systems, self-parking, lane-keeping, and adaptive cruise control.
Over time, the use of computer chips in cars has expanded to include a wide range of functions, such as controlling the transmission, adjusting for best engine performance, monitoring anti-lock brakes, and providing information to the driver, ignition and remote entry security systems, as well as infotainment and GPS location / route mapping.
In recent years, computer chips have been used to enable advanced features such as autonomus driving systems, self-parking, lane-keeping, and adaptive cruise control.
The first computer used in a car: the ECU (Engine Control Unit)

VW's first automotive computer (1968)
The first use of a computer in a car was simply for the purpose of engine control. Automotive manufactures began introducing early versions of computer controlled systems to perform one specific function; In 1968, Volkswagen introduced the first vehicle with a computer controlled electronic fuel injection (EFI) system - the D-Jetronic, a transistorized electronic module manufactured by Bosch. It was offered as standard equipment on their Type-3 models.
ECU's have become a standard device on most cars since the late 1970's when they became necessary due to increasingly stringent government emission standards.
Controlling the engine is the most processor-intensive job on your car, and the engine control unit is the most powerful computer on most cars. The ECU uses closed-loop control, a control scheme that monitors outputs of a system to control the inputs to a system, managing the emissions and fuel economy of the engine (as well as a host of other parameters).
Gathering data from dozens of different sensors, the ECU knows everything from the coolant temperature, to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
With this data, the ECU performs millions of calculations each second, including looking up values in tables, calculating the results of long equations to decide on the best spark timing and determining how long the fuel injector is open. The ECU does all of this to ensure the lowest emissions and best mileage.
ECU's have become a standard device on most cars since the late 1970's when they became necessary due to increasingly stringent government emission standards.
Controlling the engine is the most processor-intensive job on your car, and the engine control unit is the most powerful computer on most cars. The ECU uses closed-loop control, a control scheme that monitors outputs of a system to control the inputs to a system, managing the emissions and fuel economy of the engine (as well as a host of other parameters).
Gathering data from dozens of different sensors, the ECU knows everything from the coolant temperature, to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
With this data, the ECU performs millions of calculations each second, including looking up values in tables, calculating the results of long equations to decide on the best spark timing and determining how long the fuel injector is open. The ECU does all of this to ensure the lowest emissions and best mileage.
Motorola, Intel and others team up with the car makers...
Putting the first Microprocessor chips in cars
 Ford & Motorola PTEC Automotive Microcontroller chips (1994)
Ford & Motorola PTEC Automotive Microcontroller chips (1994)
In 1976, General Motors (GM) announced a new partnership with Motorola Semiconductor to develop a Custom Microcomputer for use in their vehicles. By 1981, all GM vehicles would be equipped with their new Computer Command Control System ("CCC") emission control system that featured an ECM (Electronic Control Module) that featured a Motorola 6802 based 8-bit microprocessor manufactured by Delco Electronics.
By 1986, Delco Elctronics was reported to have been manufacturing automotive Integrated Circuits at a rate of 250,000 per day. During the late 1980's, GM and Chrysler ECM's would both begin using the 16-bit Motorola 68HC11 microcontroller chip in their vehicles.
In 1983, Intel and Ford started a joint venture building EEC ( Electronic Engine Control) units now known as ECU (Electronic control Units). These ECU's used custom Intel 8061 microcontroller chips (a derivative of the Intel 8096 Micro-controller) and later used 8065, 83251, 8051, & 80515 microcontroller chips for its processing functions. The 8061 micro-controllers and its derivatives were used in almost all Ford automobiles built from 1983 thru 1994.
In 1985, Ford Microelectronics announced they would start to design and oversee the manufacture of gallium arsenide based Integrated Circuits at their Colorado Springs CO. plant for use in their own cars and aerospace products. Ford Microelectronics was formed in 1982 to develop custom integrated circuits for automotive uses and for Ford Aerospace.
In 1994, in a last attempt to save the slowing EEC IV microcontroller, Ford used two Intel 8065 16-bit chips inside the controller. Shortly thereafter, Ford would be ready to end their long use of Intel micro-controllers and transition to using Motorola's new 32-bit PTEC controllers. In 2005, Intel announced they were discontinuing production of all automotive versions of their microcontroller chips.
Previously in 1991, Ford's Electronics Division had announced they would partner with Motorola Semiconductor Products Sector to supply them with future electronic engine & transmission microcontroller chips to be used in Ford's upcoming Powertrain Electronics Controller (PTEC). The PTEC controller was originally going to use the MC88300 32-bit embedded RISC chip that Motorola had in development but would later cancel. Ford choose instead to use Motorola's new custom designed 32-bit RISC based PowerPC processor chip. PTEC microcontrollers were used in Ford vehicles starting in 1994, replacing the Intel designed EEC IV microcontroller chips that Ford had used since back in 1983.
In 1976, General Motors (GM) announced a new partnership with Motorola Semiconductor to develop a Custom Microcomputer for use in their vehicles. By 1981, all GM vehicles would be equipped with their new Computer Command Control System ("CCC") emission control system that featured an ECM (Electronic Control Module) that featured a Motorola 6802 based 8-bit microprocessor manufactured by Delco Electronics.
By 1986, Delco Elctronics was reported to have been manufacturing automotive Integrated Circuits at a rate of 250,000 per day. During the late 1980's, GM and Chrysler ECM's would both begin using the 16-bit Motorola 68HC11 microcontroller chip in their vehicles.
In 1983, Intel and Ford started a joint venture building EEC ( Electronic Engine Control) units now known as ECU (Electronic control Units). These ECU's used custom Intel 8061 microcontroller chips (a derivative of the Intel 8096 Micro-controller) and later used 8065, 83251, 8051, & 80515 microcontroller chips for its processing functions. The 8061 micro-controllers and its derivatives were used in almost all Ford automobiles built from 1983 thru 1994.
In 1985, Ford Microelectronics announced they would start to design and oversee the manufacture of gallium arsenide based Integrated Circuits at their Colorado Springs CO. plant for use in their own cars and aerospace products. Ford Microelectronics was formed in 1982 to develop custom integrated circuits for automotive uses and for Ford Aerospace.
In 1994, in a last attempt to save the slowing EEC IV microcontroller, Ford used two Intel 8065 16-bit chips inside the controller. Shortly thereafter, Ford would be ready to end their long use of Intel micro-controllers and transition to using Motorola's new 32-bit PTEC controllers. In 2005, Intel announced they were discontinuing production of all automotive versions of their microcontroller chips.
Previously in 1991, Ford's Electronics Division had announced they would partner with Motorola Semiconductor Products Sector to supply them with future electronic engine & transmission microcontroller chips to be used in Ford's upcoming Powertrain Electronics Controller (PTEC). The PTEC controller was originally going to use the MC88300 32-bit embedded RISC chip that Motorola had in development but would later cancel. Ford choose instead to use Motorola's new custom designed 32-bit RISC based PowerPC processor chip. PTEC microcontrollers were used in Ford vehicles starting in 1994, replacing the Intel designed EEC IV microcontroller chips that Ford had used since back in 1983.
Where Semiconductors are used inside Modern Automobiles
|
Powertrain:
Electronic System:
Safety and Control:
Comfort and Control:
|
Chassis:
Networking:
Infotainment:
Security and control:
|
History of Computers in Cars
- 1968 - Volkswagen introduces the first consumer vehicle available with a computer - a transistorized, electronically-controlled, fuel injection system.
- 1969 - Ford introduces their first computer controlled anti-skid system.
- 1971 - General Motors introduces their first computer controlled transmission.
- 1973 - All Chrysler models now come with an Electronic Engine Control (EEC).
- 1974 - Ford introduces their first EEC-1 system, using a Toshiba TLCS-12 12-bit microprocessor.
- 1976 - General Motors and Motorola team up to create a custom microcomputer for use in their vehicles.
- 1976 - Intel first enters the market for automotive engine controller chips.
- 1977 - Oldsmobile introduces a digital computer to control ignition timing in there Toronado model.
- 1978 - Cadillac introduces a microprocessor controlled "trip computer" in there Seville model, powered by a custom Motorola 6802 Microprocessor.
- 1978 - Ford's first Electronic Engine Control systems (the Ford EEC-1, and ECC-2) debuts in select Lincoln models, using 8-bit chips manufactured by Toshiba.
- 1978 - Mercedes-Benz and BOSCH introduce the world's first anti-lock break system (ABS).
- 1979 - Ford Electronics ECU's are using a custom version of Intel's 8049 8-bit microcontroller, the Intel 80A49H.
- 1979 - Bosch introduces their "Motronic" ECU with a Siemens manufactured 8051 microcontroller chip for use in Porsche, Volvo and BMW cars.
- 1980 - Ford introduces their Electronic Engine Control III (EEC-III) system, using a 12-bit Motorola 67002 microcontroller chip.
- 1980 - Delphi Automotive Systems Corp. starts producing Emission Modules & Control Units.
- 1981 - General Motors introduces their "Computer Command Control" (CCC) system featuring a Motorola 6802 based ECM with emissions control.
- 1983 - Ford introduces “the world’s most advanced automotive computer”, their EEC-IV Engine control system, using a custom 16-bit Intel 8061 microcontroller chip.
- 1986 - Newly formed Hypertech, introduces their first "Power Chip", allowing car owners to improve engine performance by upgrading the PROM chip in there ECU.
- 1986 - Carnegie Mellon University's "Navlab 1" becomes first computerized self-driving, autonomous car.
- 1986 - Chrysler introduces multiplexing wire communication modules with chips supplied from Harris Semiconductor.
- 1987 - First automotive micro-controller chips produced to CAN vehicle bus standards by Intel and Philips Semiconductor.
- 1990 - Delco Electronics builds it's 50 millionth ECM (Engine control module).
- 1993 - SAAB introduces their "Trionic" engine management system that uses a Motorola 68332 16/32-bit microprocessor.
- 1991 - Ford and Motorola form partnership to design & produce their PTEC powertrain & transmission micro-controllers.
- 1994 - Ford replaces their Intel designed EEC IV engine management microcontrollers with Motorola based PTEC microcontroller systems.
- 1998 - Ford enters into a license agreement for a Neural Network learning chip desinged by NASA's JPL that can improve gas mileage and reduce emissions in cars.
- 1999 - Israeli startup Mobileye is founded, a pioneer in computer vision technology for automobiles.
- 2000 - Ford Microelectronics Inc. (FMI) is acquired by Intel Corp.
- 2004 - Mobileye launches their first EyeQ chip, used in vehicles to prevent collisions.
- 2009 - Google starts up their new self-driving car project, a modified Toyota Prius, using Intel processors.
- 2010 - One of the world's largest automotive chip makers, Renesas, is formed by the merger of Hitachi, Mitsubishi Electric, and NEC electronics.
- 2012 - Google receives the first license issued in the United States for a self-driving car to operate on public roads in the state of Nevada.
- 2012 - NVIDIA announces their Tegra 3 chip will be used in Audi's In-Vehicle Infotainment systems and digital display.
- 2014 - First commercially available self-driving vehicle introduced - The Navia shuttle.
- 2014 - Apple begins working on their electric car project codenamed "Project Titan" .
- 2015 - Daimler's "Freight-liner Inspiration" becomes First self-driving, semi-autonomous, Commercial Semi Truck.
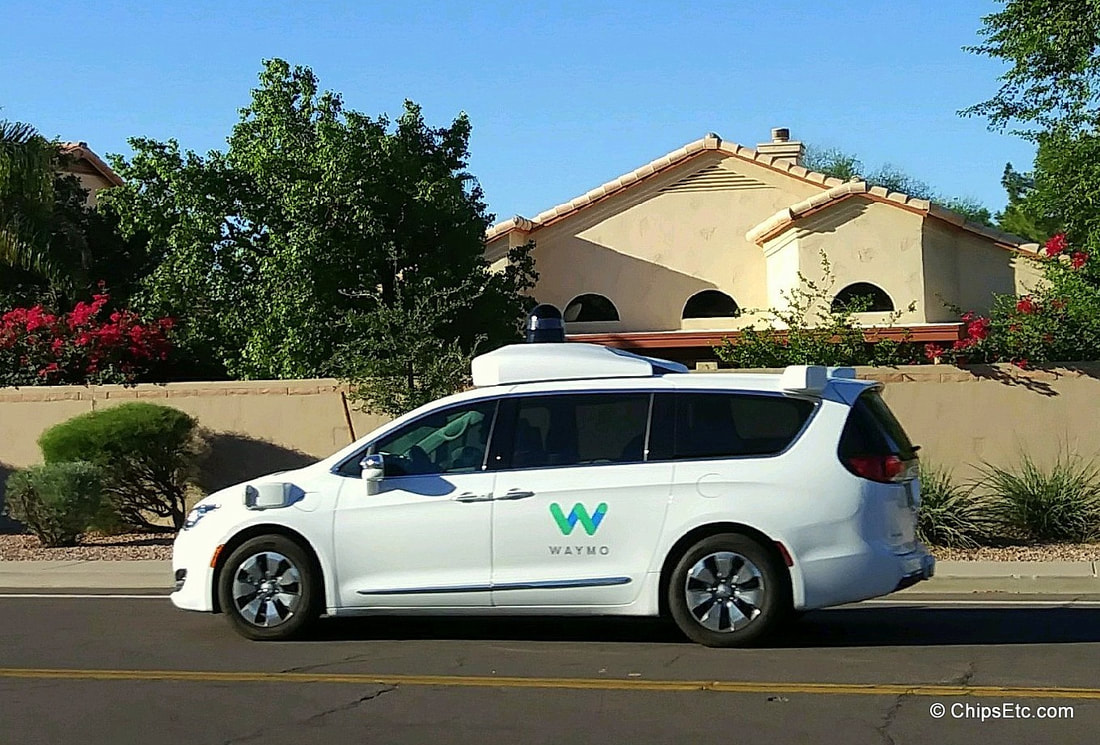
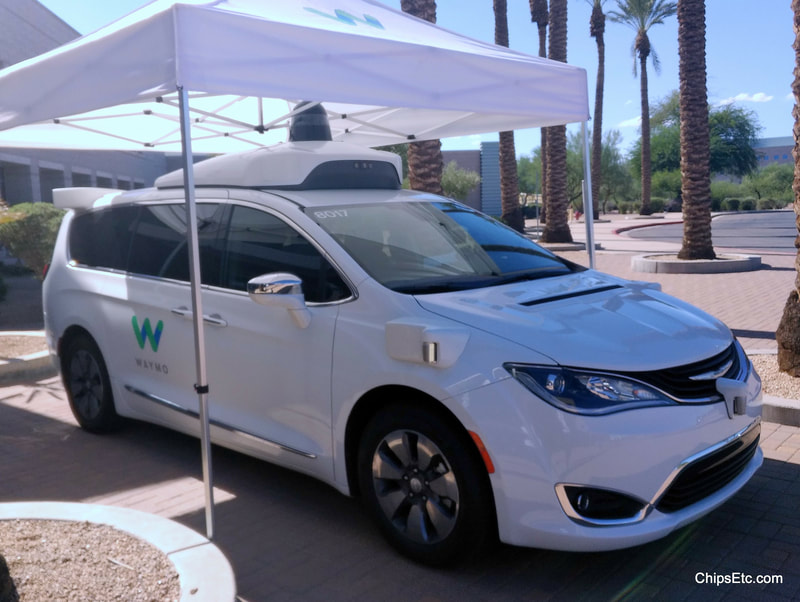
- 2016 - Google's self-driving Car project gets renamed as Waymo, and is now under Alphabet Corp.
- 2016 - Tesla begins using Nvidia's Drive PX 2 computing boards with Tegra X2 SoC chips powering their Autopilot system.
- 2016 - Audi's A8 becomes first production sedan offered with Level 3 autonomous driving technology.
- 2016 - Apple's electric car project team changes focus to creating an autonomous self-driving car.
- 2017 - Waymo and Intel announce collaboration on development of self-driving cars using Intel Xeon CPU's and programmable chips (FPGAs) in Wamo's new fleet of self-driving Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid minivans.
- 2017 - Toyota announces they will start using Nvidia GPU chips to power the A.I. in their self-driving cars.
- 2017 - Tesla "Semi" introduced, their first model of all electric, autonomous self driving, freight trucks.
- 2017 - Intel Corp. acquires Mobileye, a pioneering developer of vision-based advanced driver assistance systems.
- 2018 - Intel’s Mobileye introduces their EyeQ5 processor, a SoC chip designed for fully autonomous vehicles.
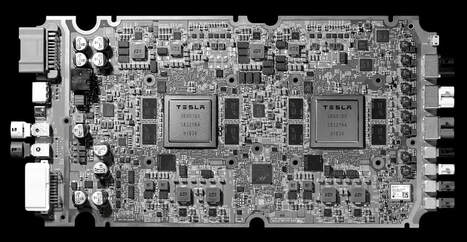
- 2019 - Tesla starts shipping Model S and X cars with their new Full Self-Driving Computer (FSD), which is powered by custom Tesla designed microprocessors, manufactured by Samsung.
- 2019 - Volvo announces they will start using Nvidia's Drive AGX Pegasus computing boards in their Polestar 2 electric cars with driver and parking assistance .
- 2019 - Computer chips now make up 4% of the cost of materials to manufacture a premium vehicle. Intel predicts by 2030 that cost will grow to 20%.
- 2020 - Infineon passes NXP semiconductoras the world's largest automotive chip maker after aquiring Cypress semiconductor.
- 2021 - Luxury Electric car maker Lucid Motors announces their "DreamDrive" Level 2 driver assistance system, with future capability to do Level 3 autonomous driving functions.
- 2021 - Volume production begins on Lucid Motor's first luxury electric vehicle - the 1,111 horsepower "Dream Edition" of their Lucid Air Sedan.
- 2021 - Tesla announces their ‘Tesla Vision’, a computer vision auto-pilot system using external cameras, replacing their front mounted radar system.
- 2021 - Numerous automotive manufactures, including GM & Ford, temporarily halt, or reduce vehicle production due to a global automotive computer chip shortage.
- 2021 - TSMC announces they will increase production of automotive chips by 60% to help with global auto chip shortages.
- 2021 - Intel announces they will expand their custom foundry capacity to produce automotive chips for automotive makers dealing with chip shortages.
- 2021 - The average new car now has over 50 computer systems inside. Gas powered cars now have over 1000 semiconductor chips inside, and Electric cars up to 3000 semiconductor chips inside.
- 2021 - Apple supplier Foxconn (Taiwan) introduces prototype versions of their own line of electric vehicles.
- 2021 - Hertz rental car company orders 100,000 Tesla Model 3 electric cars to create their new electric rental car fleet buy the end of 2022.
- 2021 - Ford Motor Co. announces they have reach a strategic agreement with chip foundry GlobalFoundries Inc. for manufacturing their in-house designed automotive chips in the future.
- 2021 - General Motors announces they are working with Qualcomm, STM, STSMC, Renaissance, On Semi, NXP Semiconductor and Infineon to co-develop a new family of microcontroller chips that combine multiple system functions, potientially reducing the amount of chips required in future GM cars by 95%.
- 2021 - Samsung announces the world's first dedicated 5G network connectivity chip for automobiles, the Exynos Auto T5123. It uses two ARM Cortex-A55 CPU cores.
- 2022 - Intel creates new Automotive group under it's Intel Foundry Services Division to focus on manufacturing automotive computer chips.
- 2022 - Intel Corp. spins off Mobileye with it's own inital public stock offering listing on NASDAQ. 50 automotive companies are now using the their self-driving technology across 800 vehicle models.
Intel's Mobileye Autonomous vehicle display created for the 2018 Consumer Electronics Show
Today's Automobiles contain hundreds of Computer Chips...
Self-Driving cars will add even more computer systems to cars
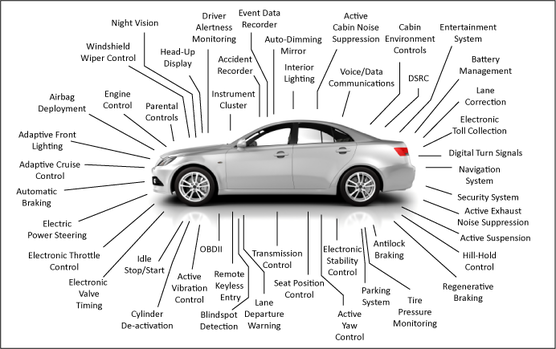
Computers in modern cars monitor many different systems
Today, a car can have well over 50 seperate computer systems monitoring & controlling everything from ride handling, engine performance and efficiency, safety sensors, on-board entertainment & Communication systems, as well as computer vision and guidance systems in self-driving cars. Computer feedback systems driving Artificial Intelligence (A.I.) in todays self-driving cars can include numerous sensor inputs including radar and lidar, ultrasonic sensors, and external cameras.
Numerous automakers including Ford, GM, Tesla, VW, BMW, Lucid Motors, Rivian, Porsche, Mercedes, Volvo / Polestar, Subaru and others are developing or now producing their own models of autonomous self-driving cars which will only add to the growing number of computers found inside a car. Tech companies involved in developing the computer systems for these autonomous cars include, Tesla, AMD, Ford, Lyft, Google / Alphabet (Waymo), Nvidia, Apple, NURO, and Mobileye / Intel.
List of current automotive semiconductor suppliers that manufacture chips for cars
NXP Semiconductor, Renesas, Infineon, STMicroelectronics (STM), Bosch, Texas Instruments, Microchip, ROHM, ON Semiconductor, Samsung, MIPS, Qualcomm, Toshiba, Micron Technology, Taiwan Semiconductor, GlobalFoundries, Renaissance, and Intel.
The majority of todays Automotive chips are microcontrollers still being manufactured using older 40nm, 90nm & 130nm Semiconductor technology processes that matured more than 15 years ago, unlike the constantly improving chip technologies (14nm, 10nm and 7nm technology) used in many of todays processors ued in desktop PCs., servers, smartphones, and laptops.
Numerous automakers including Ford, GM, Tesla, VW, BMW, Lucid Motors, Rivian, Porsche, Mercedes, Volvo / Polestar, Subaru and others are developing or now producing their own models of autonomous self-driving cars which will only add to the growing number of computers found inside a car. Tech companies involved in developing the computer systems for these autonomous cars include, Tesla, AMD, Ford, Lyft, Google / Alphabet (Waymo), Nvidia, Apple, NURO, and Mobileye / Intel.
List of current automotive semiconductor suppliers that manufacture chips for cars
NXP Semiconductor, Renesas, Infineon, STMicroelectronics (STM), Bosch, Texas Instruments, Microchip, ROHM, ON Semiconductor, Samsung, MIPS, Qualcomm, Toshiba, Micron Technology, Taiwan Semiconductor, GlobalFoundries, Renaissance, and Intel.
The majority of todays Automotive chips are microcontrollers still being manufactured using older 40nm, 90nm & 130nm Semiconductor technology processes that matured more than 15 years ago, unlike the constantly improving chip technologies (14nm, 10nm and 7nm technology) used in many of todays processors ued in desktop PCs., servers, smartphones, and laptops.
Tesla designed "full self-driving computer" (FSD) w dual processors manufactured by Samsung
The Tesla HW3 (hardware 3) full Self driving computer (FSD) board currently being manufactured by Samsung features two separate SOC chips, each containing ARM cortex A72s 12-core processor chips.
The dual processor configuration allows for self-checking and validation, offering redundancy and safety.