Diodes
Types of Diodes
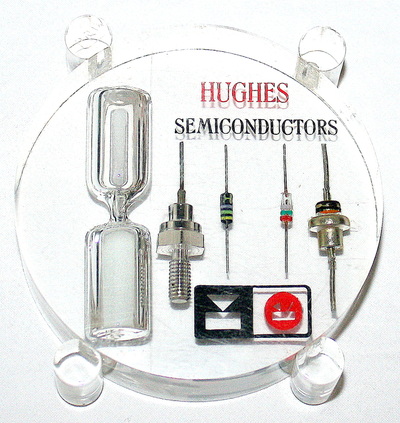
A Diode is a semiconductor component that allows electricity in a circuit to flow in one direction only and blocks the flow of electricity in the opposite direction.
Diodes were originally created in the 1950's to replace vacuum tubes in applications of low power rectification.
The Diode is made of a semiconducting material (Silicon, Germanium, or Selenium) and contains two electrodes called the Anode and the Cathode.
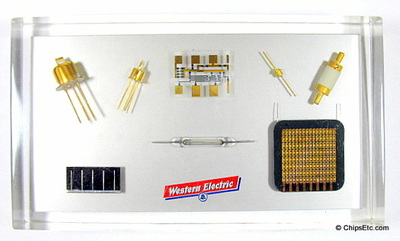
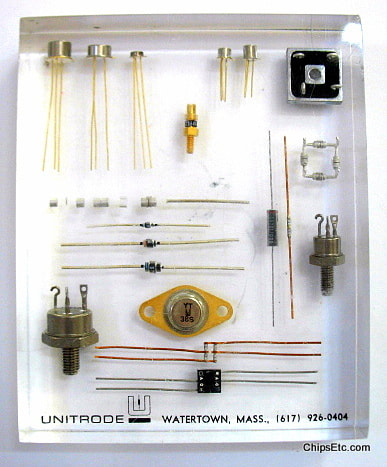
There are many different types of diodes: Generic, Schottky, Shockley, Constant current, Zener, Light-emitting, Photo, Step recovery, Tunnel, Varactor, PIN & Vacuum tube.
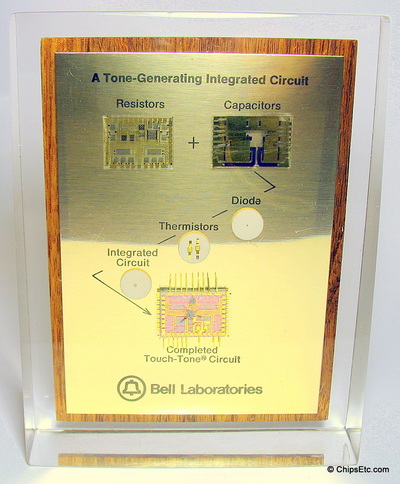
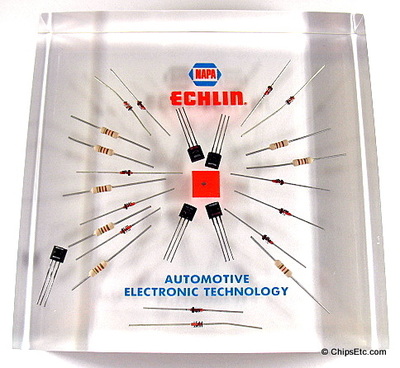
Diodes can be used in numerous electronic circuit applications including: switches, rectifiers, signal limiters, voltage regulators, signal modulators, signal mixers, signal de-modulators, and oscillators.
Diodes are also used in solar cell circuits, and in semiconductor circuits including CCD imaging chips to produce electrical current when visible light, infrared, or ultraviolet energy strikes them, and in LED (light emitting) diodes which emit visible light or IR energy when current passes through them.